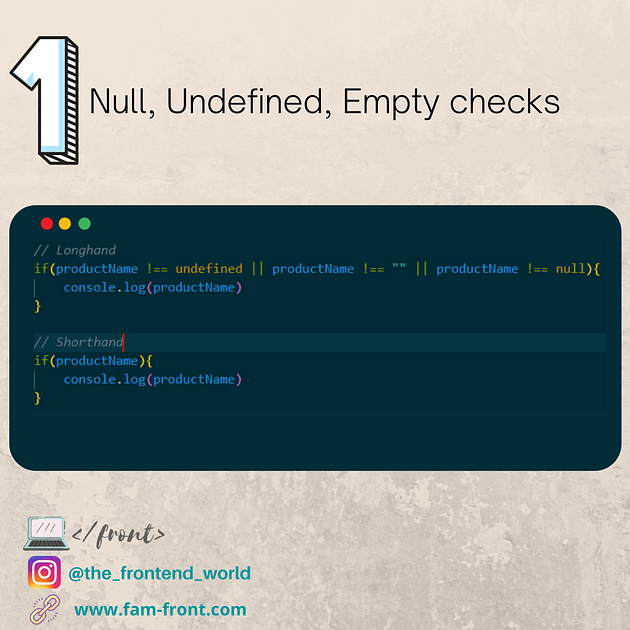
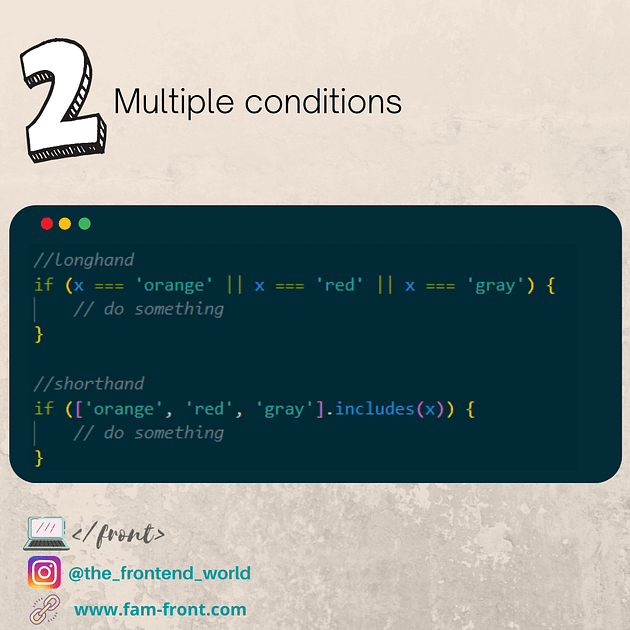
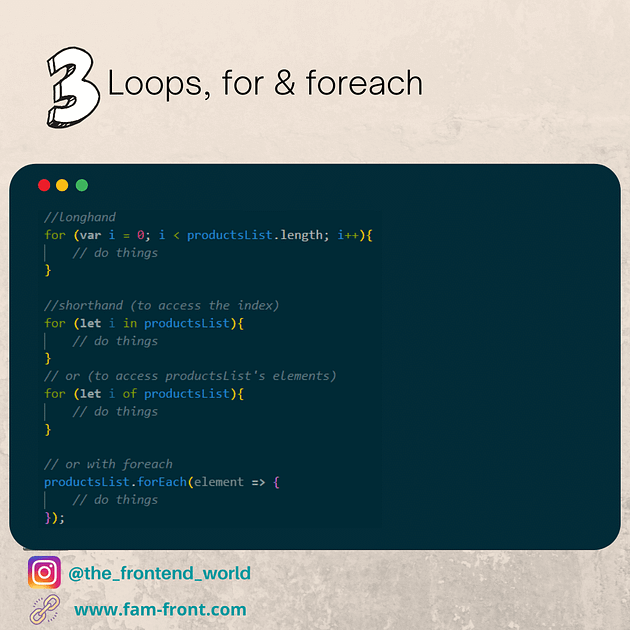
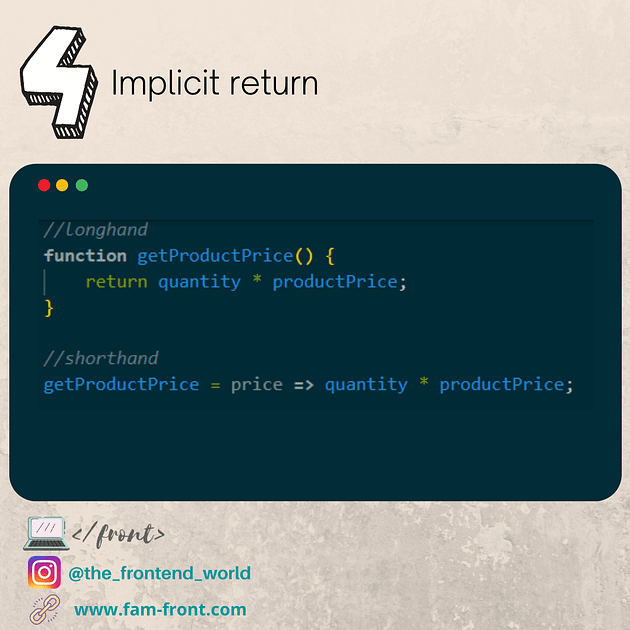
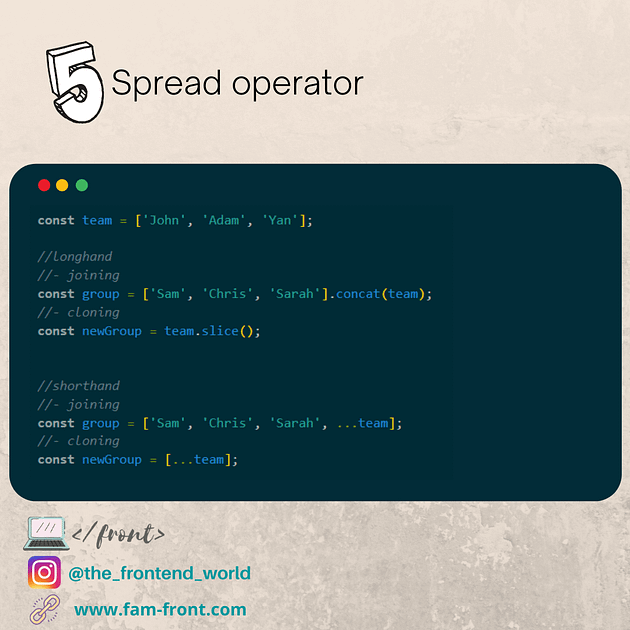
endsWith (mozilla.org)
어떤 문자열에서 특정 문자열로 끝나는지를 확인할 수 있으며, 그 결과를 true 혹은 false로 반환한다.
var str = 'To be, or not to be, that is the question.';
console.log(str.endsWith('question.'));
console.log(str.endsWith('to be'));
console.log(str.endsWith('to be', 19));
includes (mozilla.org)
하나의 문자열이 다른 문자열에 포함되어 있는지를 판별하고, 결과를 true 또는 false 로 반환합니다.
var str = 'To be, or not to be, that is the question.';
console.log(str.includes('To be'));
console.log(str.includes('question'));
console.log(str.includes('nonexistent'));
console.log(str.includes('To be', 1));
console.log(str.includes('TO BE'));
indexOf (mozilla.org)
호출한 String 객체에서 주어진 값과 일치하는 첫 번째 인덱스를 반환합니다. 일치하는 값이 없으면 -1을 반환합니다.
const paragraph = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog. If the dog barked, was it really lazy?';
const searchTerm = 'dog';
const indexOfFirst = paragraph.indexOf(searchTerm);
console.log(`The index of the first "${searchTerm}" from the beginning is ${indexOfFirst}`);
// expected output: "The index of the first "dog" from the beginning is 40"
console.log(`The index of the 2nd "${searchTerm}" is ${paragraph.indexOf(searchTerm, (indexOfFirst + 1))}`);
// expected output: "The index of the 2nd "dog" is 52"
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('Blue');
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('Blute');
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('Whale', 0);
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('Whale', 5);
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('Whale', 7);
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('');
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('', 9);
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('', 10);
'Blue Whale'.indexOf('', 11);
lastIndexOf (mozilla.org)
주어진 값과 일치하는 부분을 fromIndex로부터 역순으로 탐색하여, 최초로 마주치는 인덱스를 반환합니다. 일치하는 부분을 찾을 수 없으면 -1을 반환합니다.
const paragraph = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog. If the dog barked, was it really lazy?';
const searchTerm = 'dog';
console.log(`The index of the first "${searchTerm}" from the end is ${paragraph.lastIndexOf(searchTerm)}`);
// expected output: "The index of the first "dog" from the end is 52"
'canal'.lastIndexOf('a');
'canal'.lastIndexOf('a', 2);
'canal'.lastIndexOf('a', 0);
'canal'.lastIndexOf('x');
'canal'.lastIndexOf('c', -5);
'canal'.lastIndexOf('c', 0);
'canal'.lastIndexOf('');
'canal'.lastIndexOf('', 2);
match (mozilla.org)
문자열이 정규식과 매치되는 부분을 검색합니다.
var str = 'For more information, see Chapter 3.4.5.1';
var re = /see (chapter \d+(\.\d)*)/i;
var found = str.match(re);
console.log(found);
matchAll (mozilla.org) ES2020
returns an iterator of all results matching a string against a regular expression, including capturing groups.
const regexp = /t(e)(st(\d?))/g;
const str = 'test1test2';
const array = [...str.matchAll(regexp)];
console.log(array[0]);
// expected output: Array ["test1", "e", "st1", "1"]
console.log(array[1]);
// expected output: Array ["test2", "e", "st2", "2"]
const regexp = RegExp('foo[a-z]*','g');
const str = 'table football, foosball';
let match;
while ((match = regexp.exec(str)) !== null) {
console.log(`Found ${match[0]} start=${match.index} end=${regexp.lastIndex}.`);
}
padEnd (mozilla.org)
현재 문자열에 다른 문자열을 채워, 주어진 길이를 만족하는 새로운 문자열을 반환합니다. 채워넣기는 대상 문자열의 끝(우측)부터 적용됩니다.
const str1 = 'Breaded Mushrooms';
console.log(str1.padEnd(25, '.'));
// expected output: "Breaded Mushrooms........"
const str2 = '200';
console.log(str2.padEnd(5));
// expected output: "200 "
'abc'.padEnd(10);
'abc'.padEnd(10, "foo");
'abc'.padEnd(6, "123456");
'abc'.padEnd(1);
replace (mozilla.org)
"cat, cat, cat, bird".replace("cat", (i) => i + "dog"); // returns "catdog, cat, cat, bird"replaceAll (mozilla.org)
"cat, cat, cat, bird".replaceAll("cat", (i) => i + "dog"); // returns "catdog, catdog, catdog, bird"search (mozilla.org)
"cat, dog, cat".search("dog"); // returns 5
// With a regex
"cat, dog, cat".search(/dog/g); // returns 5slice (mozilla.org)
"This is a string I want to slice".slice(27); // returns 'slice'
"This is a string I want to slice".slice(27, 28); // returns 's'
// And we can work backwards with negative values such as
"This is a string I want to slice".slice(-5); // returns "slice"
"This is a string I want to slice".slice(-5, -1); // returns "slic"
startsWith (mozilla.org)
"Hello".startsWith("h"); // true
"Hello".startsWith("e"); // false
// With optional starting index
"Hello".startsWith("e", 1); // true